Typical Causes and Treatments of Hearing Loss
A hearing impairment is a full or partial inability to detect or perceive certain frequencies in the normal range of hearing.
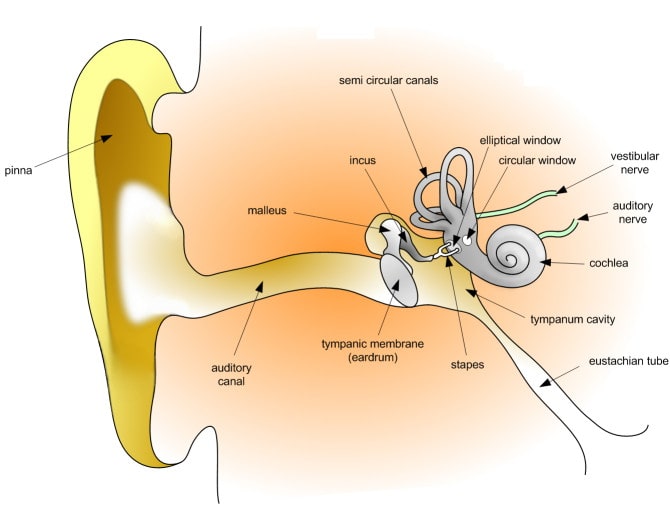
There are three types of hearing loss: conductive, sensorineural or mixed (a combination of both).
Conductive hearing loss can result from problems affecting the outer ear or the middle ear. Common problems include cerumen (earwax) buildup, ear infections, otosclerosis (abnormal bone growth within the middle ear) or a perforation of the eardrum.
Sensorineural hearing loss is a problem of the inner ear. The majority of these cases result from abnormalities of the hair cells and their function. Aging, illness, hereditary factors, long-term exposure to loud noises and ototoxic drugs (drugs that damage the hearing system) are all common causes of sensorineural hearing loss.
Conductive hearing loss can usually be treated medically with medication or surgery. Hearing aids however, are most recommended for sensorineural hearing loss.
Tinnitus – any noise that comes from within the ear and not an external source – is also a common hearing impairment. It is often described as buzzing, ringing or humming. It can be constant or intermittent.
Tinnitus can be caused by many of the same factors as sensorineural hearing loss, such as aging, exposure to loud noises, illness and ototoxicity. The most common therapy for tinnitus is tinnitus-masking, which is achieved through the use of hearing aids.
